Adolescence
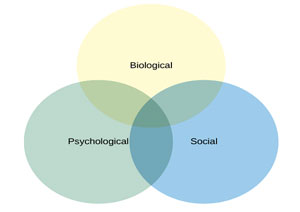
Adolescence is a transitional phase for physical and psychological growth
that generally occurs during the period from puberty to legal adulthood.
Promoting healthy behaviors during adolescence, and taking steps to protect
young people from health risks are critical for the prevention of health problems in adulthood,
and for countries’ future health and ability to develop and thrive.
Special Characters
- Rapid physical growth & development.
- Physical, social & psychological development.
- Sexual maturity & onset of sexual activity.
- Experimentation.
- Transition from total socioeconomic dependence to relative independence.
- Onset of reproductive cycle.
- Development of adult mental process & adult identity.
Rapid physical growth and development
Physical growth
- Skeletal growth - Secondary growth spurt – 25% of adult height
- Body composition - Weight gain - Increase in adipose tissue in girls
- Increase muscle mass
Physical Changes in boys
The changes that boys may notice between 11-17 years are:
- A rapid growth in height
- Hair growth under arms, between legs and on the face
- A widening of the shoulders
- Muscles becoming more developed creating an angular outline to the body
- A much deeper voice – called ‘breaking’ and
- The enlarging of the reproductive organs and sperm production beginning
Hormonal changes –
- FSH, LH, Estradiol, Testosterone, adrenal androgens.
- Secondary sexual characters
- Breast development
- Pubic hairs
- Development of genitilia
These changes happen over 3- 4 years
Psychosocial development
- Less interest in parental activities
- Mood swings.
- Intense relationship with same & opposite sex friends.
- Increased cognitive function.
- Increased need for privacy.
- Lack of impulse control.
- Increased intellectual ability.
- Risk- taking behavior.
Sexual changes
Curious to know about their own as well opposite gender
Main health issues are
- Unintentional injuries are the leading cause of death and disability among
adolescents.
- Depression is one of the leading causes of illness and disability. Violence,
poverty, humiliation and feeling devalued.
- Strong ties between adolescents and their families are most important.
- Promoting nurturing relationships between parents and children early in life.
- Interpersonal violence varies substantially by world region.
Nutrition and micronutrient deficiencies
- Dry hair, Pale skin, Pale lips, puffy eyes, Bleeding gums.
- Iron deficiency anaemia was the second leading cause of years lost by adolescents to death
and disability in 2016.
- Iron and folic acid supplements.
- Regular deworming.
Developing healthy eating habits in adolescence are foundations for good health in adulthood.
Many boys and girls in developing countries enter adolescence undernourished, making them more
vulnerable to disease and early death. At the other end of the spectrum, the number of
adolescents who are overweight or obese is increasing in low-, middle- and high-income
countries.
Physical activity provides fundamental health benefits for adolescents, including improved
cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, bone health, maintenance of a healthy body weight, and
psychosocial benefits. WHO recommends for adolescents to accumulate at least 60 minutes of
moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity daily,
Globally, only 1 in 5 adolescents are estimated to meet these guidelines.